Turkey is a unique country both geographically and culturally. It is located at the crossroads between Europe and the Middle East and it has been influenced by both regions for centuries. As a result, many languages have been spoken in Turkey over the years. Today, the most widely spoken language in Turkey is Turkish.
Turkish is a Turkic language like Azerbaijani, Turkmen and Uzbek, but it has also been heavily influenced by other languages like Arabic, French and Persian. It is the native language of the majority of the population and it is the only official language of the country. Turkish is written using a variant of the Latin alphabet and it is also used as a lingua franca among the many different ethnic groups in the country.
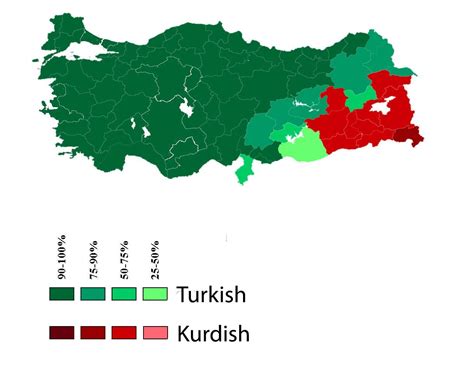
In addition to Turkish, there are several other minority languages spoken in Turkey. These include Kurdish, Laz, Circassian, and Georgian. The presence of these languages dates back to the time of the Ottoman Empire when many different ethnic groups lived within its borders. However, due to the assimilation policies of the early Republic of Turkey, these languages are now limited to certain regions and are spoken mainly by older generations.
While Turkish is the official language of Turkey, English is becoming increasingly popular. English is seen as a key to economic prosperity, so it is taught in schools and is widely used in business. Other popular languages in Turkey include German and French, which are taught in some schools and universities.
Turkish is a fascinating and complex language with a rich history. It is the main language of communication in Turkey and it is used in all areas of life, from business and politics to literature and music. Despite the presence of other languages, Turkish is the language of the majority and it is only set to become more popular in the years to come.
The Turkish Language in Turkey
Turkey is a country located in the Eurasian region and is known for its diverse cultures, customs, and languages. In terms of language, it is mainly spoken in the Turkish language, but there are other languages that are spoken in the country as well. The Turkish language has been the official language of Turkey since the founding of the Republic of Turkey in 1923, and it is used in all areas of life in the country.
The Turkish language is a member of the Turkic languages, which is a branch of the Altaic languages. It is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages and is spoken by more than 87 million people in Turkey, as well as by about 3 million people in other countries. It is written in the Latin alphabet, which was adopted in 1928 as part of the modern Turkish language reform.
The Turkish language is characterized by a variety of dialects and accentuates, which vary from region to region. The different dialects are divided into three main groups: Anatolian, which is mainly spoken in the western parts of the country; Black Sea, which is spoken in the northern parts; and Thrace, which is spoken in the southeastern parts. The language also features a number of loanwords from other languages, such as Arabic, Persian, French, and Greek, due to the country’s multi-cultural history.
In terms of grammar, Turkish is an agglutinative language, which means that it is made up of words that are formed by the addition of suffixes to a root word. This makes Turkish a relatively easy language to learn, as the suffixes are easy to remember.
In terms of pronunciation, Turkish has a very specific set of rules. For example, the letter “ı” is always pronounced as a short “e”, and the letter “u” is always pronounced as a long “o”. Additionally, the letter “y” is always pronounced as a soft “i”.
The Turkish language has a rich literary tradition, with some of the most famous Turkish writers being Orhan Pamuk, Yusuf Atılgan, and Elif Şafak. Turkish literature has also been heavily influenced by the country’s diverse cultural history, as well as the unique blend of Western and Eastern influences.
Learning the Turkish language can be a rewarding experience, as it can open up many new opportunities in the country. Whether you are looking to travel, work, or study in Turkey, having an understanding of the language will certainly be beneficial.
Understanding the Different Variants of Turkish
Turkey is a multi-cultural and multi-lingual country, and its rich history has made it a global melting pot of different cultures, religions, and languages. There are several languages spoken in Turkey, but the most widely spoken is Turkish. It is the official language of the country and is spoken by the vast majority of citizens. But what are the different variants of Turkish spoken in Turkey?
The various dialects of Turkish can be divided into two main categories: Eastern and Western. The Eastern dialect is spoken in the eastern part of the country, while the Western dialect is spoken in the western part. The Eastern dialect is the most common, as it is spoken by more than 70% of the population. It is also the official language of Turkey, and is used in most official documents and conversations. The Western dialect, on the other hand, is less common and is mainly spoken by minority ethnic groups in the western part of the country.
The two most widely used variants of Turkish are Istanbul Turkish and Anatolian Turkish. Istanbul Turkish is the variant of Turkish spoken in the capital of Turkey, Istanbul, and it is considered the standard dialect. It is used in TV broadcasts and in many formal contexts. Anatolian Turkish, on the other hand, is the variant spoken in the rest of the country, and it is known for its distinct accents and pronunciations. The two variants are very similar, but there are some differences in vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation that can make it difficult to understand one another.
Other variants include the various dialects spoken in the north and east, Southeastern Anatolian, and Crimean Tatar. These variants all have their own unique characteristics, including pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary, and they can be difficult for native speakers of other variants to understand. The Crimean Tatar dialect is considered to be the most difficult to understand, as it has been heavily influenced by other languages, such as Russian, Greek, and Armenian.
If you’re looking to learn the different variants of Turkish, it’s important to understand that each variant has its own unique features and quirks. It’s also important to note that the language is constantly evolving. Therefore, it’s important to find a teacher or program that specializes in teaching the language in order to get the most out of your learning experience.
The official language of Turkey is Turkish. It is an Altaic language, related to Azerbaijani, Turkmen, and Gagauz languages.
Turkish is a language that originated from Central Asia and is now spoken in Turkey and many other countries.
Other languages spoken in Turkey include Kurdish, Circassian, Arabic, Armenian, Greek, and Georgian.
It may be difficult to learn Turkish depending on an individual’s language learning skills and background.
Yes, Turkish is the official language of Turkey.
Turkish is the most widely spoken language in Turkey.
Yes, there are various dialects of Turkish spoken in different regions of Turkey.
No, Turkish is the only official language of Turkey.
Kurdish is one of the oldest languages spoken in Turkey.
The main language used in education in Turkey is Turkish.